Unveiling Iran's Regions: A Deep Dive Into Its Diverse Map
Table of Contents
- Historical Divisions of Iran: A Look Back
- Iran on the Global Map: Geographical Context and Borders
- The Five Modern Regions of Iran
- Topography and Climate Diversity Across the Map Iran Region
- Provinces and Their Capitals: Administrative Structure
- Key Cities and Strategic Locations on the Map
- The Value of Detailed Mapping for Understanding Iran
- Beyond Borders: Iran in the International Arena
Historical Divisions of Iran: A Look Back
Understanding the current administrative landscape of Iran benefits greatly from a glance at its historical evolution. The concept of dividing territories for administrative purposes is not new to Iran, a land with a rich imperial past. The "map Iran region" has undergone significant transformations over centuries, reflecting shifting political landscapes and evolving governance needs. One notable period of administrative reorganization occurred in the mid-20th century. According to historical records, specifically the "Territorial Subdivision Act of 1316 Š./1937 (Qānūn-e taqsīmāt-e kešvar)," Iran's territory was systematically divided into ten administrative regions between 1937 and 1960. This division was a foundational step in modernizing the country's governance. For instance, what was then known as Region 7, or the "Seventh Province," directly corresponded to the present-day Fars province. This historical framework, documented in sources like "پیشینه تقسیمات کشوری ایران," provides crucial context for how the current provincial and regional system developed. These historical maps serve as invaluable resources, showcasing the administrative foresight that shaped the nation's territorial management.Iran on the Global Map: Geographical Context and Borders
To truly grasp the significance of any "map Iran region," one must first appreciate Iran's broader geographical context. Spanning an impressive area of 1,648,195 square kilometers (636,372 sq mi), Iran is a vast country, larger than Egypt but smaller than Libya. Its location at the crossroads of the Middle East, Central Asia, and the Caucasus makes it a geopolitical linchpin. A comprehensive political map of Iran not only delineates its international borders but also highlights its surrounding countries: Iraq, Turkey, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Turkmenistan, Azerbaijan, and Armenia. This proximity to multiple nations underscores Iran's role in regional stability and trade. Beyond its land borders, Iran boasts extensive coastlines on three major bodies of water: the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman to the south, and the Caspian Sea to the north. These maritime boundaries are vital for trade, energy exports, and strategic defense, further emphasizing the importance of a detailed "map Iran region" for strategic analysis. Topographically, Iran is a land of striking contrasts. A map reveals a country largely dominated by vast desert zones, notably the Kavir Desert in the central region and the Lut Desert to the east. These arid expanses are flanked by two major mountain ranges – the Alborz in the north and the Zagros in the west – which play a crucial role in shaping the country's climate and hydrology. Scattered across this predominantly dry landscape are smaller wooded areas, particularly noticeable near the Caspian coast. Understanding these geographical features is essential for interpreting any "map Iran region," as they dictate population distribution, economic activities, and infrastructure development.The Five Modern Regions of Iran
While Iran is officially divided into 31 provinces, for administrative and planning purposes, the country is also often grouped into five distinct regions. These regional groupings offer a broader perspective on the country's geographical and cultural segments, providing a useful lens through which to view the "map Iran region." These regions are designed to facilitate better coordination among provinces and enhance regional development. The five regions of Iran are: 1. **Tabriz Region (Northwest)** 2. **Tehran Region (North)** 3. **Kermanshah Region (West)** 4. **Isfahan Region (South)** 5. **Mashhad Region (East)** Each of these regions serves as a hub for its surrounding provinces, reflecting a balance of population, economic activity, and strategic importance.Tabriz: The Northwest Gateway
The Tabriz region, situated in the northwest of Iran, is a historically rich and strategically important area. It encompasses several key provinces, including Ardabil Province, East Azerbaijan Province, Gilan Province, and Kordestan Province. This region is known for its rugged terrain, vibrant cultural heritage, and significant economic contributions, particularly in trade with neighboring countries like Azerbaijan and Turkey. A "map Iran region" focusing on the northwest would highlight the mountainous landscapes, the fertile plains, and the intricate network of roads connecting it to the rest of Iran and beyond.Tehran: The Beating Heart of Iran
Tehran, the capital and largest city of Iran, anchors the northern region. Located at the foot of the majestic Alborz mountain range, Tehran is a sprawling metropolis with a population of approximately 9 million in the city proper and over 14.5 million in the greater metropolitan area. This makes it one of the most populous cities in Western Asia. The Tehran region is the political, economic, and cultural nerve center of Iran. Its position on the "map Iran region" signifies its central role in national governance, finance, and innovation. The city's extensive infrastructure, including major airports and road networks, is clearly visible on detailed maps, underscoring its connectivity and dynamism.Kermanshah and Western Iran
The Kermanshah region represents a significant portion of Western Iran, extending west of major Iranian cities like Tehran and Qom. This area is characterized by its diverse ethnic groups, rich historical sites, and agricultural significance. The "map Iran region" of the west reveals a landscape often marked by the Zagros Mountains, influencing both climate and human settlement patterns. Cities like Kermanshah have historically served as important trade routes and cultural crossroads, making this region a vital link between Iran and its western neighbors, particularly Iraq.Isfahan: The Cultural Southern Hub
Isfahan, a city renowned for its stunning Islamic architecture and rich history, serves as the hub for Iran's southern region. This region, as depicted on a "map Iran region," extends towards the central and southern parts of the country, bordering the vast desert expanses and eventually leading towards the Persian Gulf. The Isfahan region is a melting pot of traditional arts, crafts, and a significant center for tourism. Its strategic location historically facilitated trade and cultural exchange, a legacy that continues to shape its identity today.Mashhad: The Eastern Spiritual Center
The Mashhad region, located in the east of Iran, is anchored by the holy city of Mashhad, a major pilgrimage site for Shia Muslims. This eastern "map Iran region" is characterized by its proximity to Central Asian nations like Afghanistan and Turkmenistan, influencing its cultural and economic ties. The region's landscape transitions from fertile plains to more arid zones as one moves further east, reflecting the diverse topography of Iran. Mashhad's spiritual significance and its role as a regional trade hub make it a critical component of Iran's overall regional structure.Topography and Climate Diversity Across the Map Iran Region
Iran exhibits remarkable climatic diversity, a feature directly attributable to its varied topography and vast geographic position. A detailed "map Iran region" that includes topographical data vividly illustrates how mountains, deserts, and coastlines shape the country's weather patterns. Most regions of Iran experience an arid or semi-arid climate, characterized by low precipitation. Annual rainfall averages less than 250mm across much of the country. This aridity is particularly pronounced in the central and eastern desert zones, including the Kavir and Lut deserts, which are among the hottest and driest places on Earth. However, the Caspian coastal region presents a stark contrast. Thanks to the moisture-laden winds from the Caspian Sea and the barrier effect of the Alborz Mountains, this narrow strip of land receives significantly higher amounts of precipitation, often exceeding 1,000mm annually. This creates a lush, green landscape, a stark difference from the country's predominantly brown and arid interior. Understanding these climatic zones is crucial for anyone studying the "map Iran region," as they dictate agricultural practices, water resource management, and population distribution. The interplay of high mountains and vast plains also influences temperature extremes, with scorching summers in the lowlands and cold, snowy winters in the highlands.Provinces and Their Capitals: Administrative Structure
While the five regions provide a broad overview, the fundamental administrative unit of Iran is the province (Persian: استان, *ostân*). Iran is currently divided into 31 provinces, each governed from a local center, usually the largest local city, which is called the capital (Persian: مرکز, *markaz*) of that province. This granular level of division is critical for day-to-day governance and service delivery. A "map Iran region" that delves into provincial boundaries offers a more detailed understanding of the country's administrative layout. These maps often include province capitals, major cities, and key infrastructure like main roads and railroads, providing a comprehensive view of how the country is organized. Data on provinces, such as their contribution to national GDP (e.g., in 2014) or GDP per capita (e.g., in 2012), further enriches the understanding of their economic significance and development levels across the diverse "map Iran region." This administrative structure ensures that governance reaches every corner of the vast nation, adapting to local needs while adhering to national policies.Key Cities and Strategic Locations on the Map
Beyond administrative boundaries, certain cities and locations hold immense strategic and historical importance, making them prominent features on any detailed "map Iran region." Tehran, as previously mentioned, is not just the capital but also the economic and political heart. Its population density and infrastructure make it a critical node. Other major cities like Esfahan, Kermanshah, and Tabriz are not only regional centers but also possess historical significance and modern strategic value. For instance, Persepolis, the ancient ceremonial capital of the Achaemenid Empire, remains a key historical landmark, attracting scholars and tourists alike. Its location on the map reminds us of Iran's deep historical roots. Modern maps of Iran also highlight locations of strategic interest, such as nuclear facilities. Discussions and analyses often involve detailed maps showing Iran's nuclear sites and potential areas of concern, including those in cities like Tehran, Esfahan, Kermanshah, and Tabriz. Conversely, these maps might also depict locations of reported Israeli airstrikes, illustrating the complex geopolitical landscape surrounding Iran's strategic programs. Such specific mapping serves critical analytical purposes, reflecting the country's role in global security discussions. The ability to visualize these sensitive locations on a "map Iran region" is crucial for understanding current events and international relations.The Value of Detailed Mapping for Understanding Iran
The evolution of mapping technology has significantly enhanced our ability to understand complex geographies like Iran's. Modern tools have automated the process of turning geographic data into map graphics, enabling the creation of higher quality, faster, and cheaper maps than ever before. This technological advancement means that a "map Iran region" can be presented in a wide variety of map types and styles, offering diverse perspectives. Whether it's a topographic map showing mountains and deserts, a political map with international borders, or a specialized map detailing infrastructure or specific sites, the availability of diverse map collections is invaluable. These maps offer a detailed view of the country’s major regions, key infrastructure (like main roads, railroads, and major airports), and historical landmarks. They serve as a valuable resource for anyone interested in Iran, from researchers and policymakers to tourists and general readers. The ability to explore detailed maps of Iran's regions, with the possibility to download and print them, facilitates deeper learning and analysis, making it easier to visualize the country's vastness and intricate details. Online platforms like OrangeSmile tours even offer virtual excursions, allowing users to explore major sights of Iran, further demonstrating the utility of modern mapping.Beyond Borders: Iran in the International Arena
Iran's geographical position naturally places it at the center of many international discussions and relationships. Its extensive borders and maritime access make it a crucial player in regional trade, energy transit, and security dynamics. While Iran shares intimate economic ties with countries like Qatar, it may not always share similar political thoughts, as exemplified by differing stances on conflicts like the Syrian conflict. The "map Iran region" extends beyond its physical boundaries to encompass its sphere of influence and its interactions with the global community. Understanding its neighbors, its access to vital waterways like the Persian Gulf and the Caspian Sea, and its internal regional dynamics is essential for comprehending Iran's foreign policy and its role in global affairs. From trade routes to geopolitical alliances, the geographical realities depicted on a comprehensive map of Iran's regions are fundamental to interpreting its international standing and future trajectory.Conclusion
From the historical administrative divisions of the 1930s to the modern five-region grouping, the "map Iran region" tells a compelling story of a diverse and complex nation. We've journeyed through its vast deserts and towering mountain ranges, explored its varied climatic zones, and highlighted the strategic importance of its major cities and borders. Understanding Iran's geography, its administrative structure, and the unique characteristics of each region is not just an academic exercise; it's essential for anyone seeking to grasp the country's rich history, vibrant culture, and pivotal role on the global stage. We hope this comprehensive exploration has provided you with a clearer picture of Iran's fascinating regional landscape. What aspect of Iran's geography or regions do you find most intriguing? Share your thoughts in the comments below! If you're eager to delve deeper, consider exploring more detailed maps or historical documents to further your understanding of this ancient and ever-evolving land.
Philippines Maps | Printable Maps of Philippines for Download
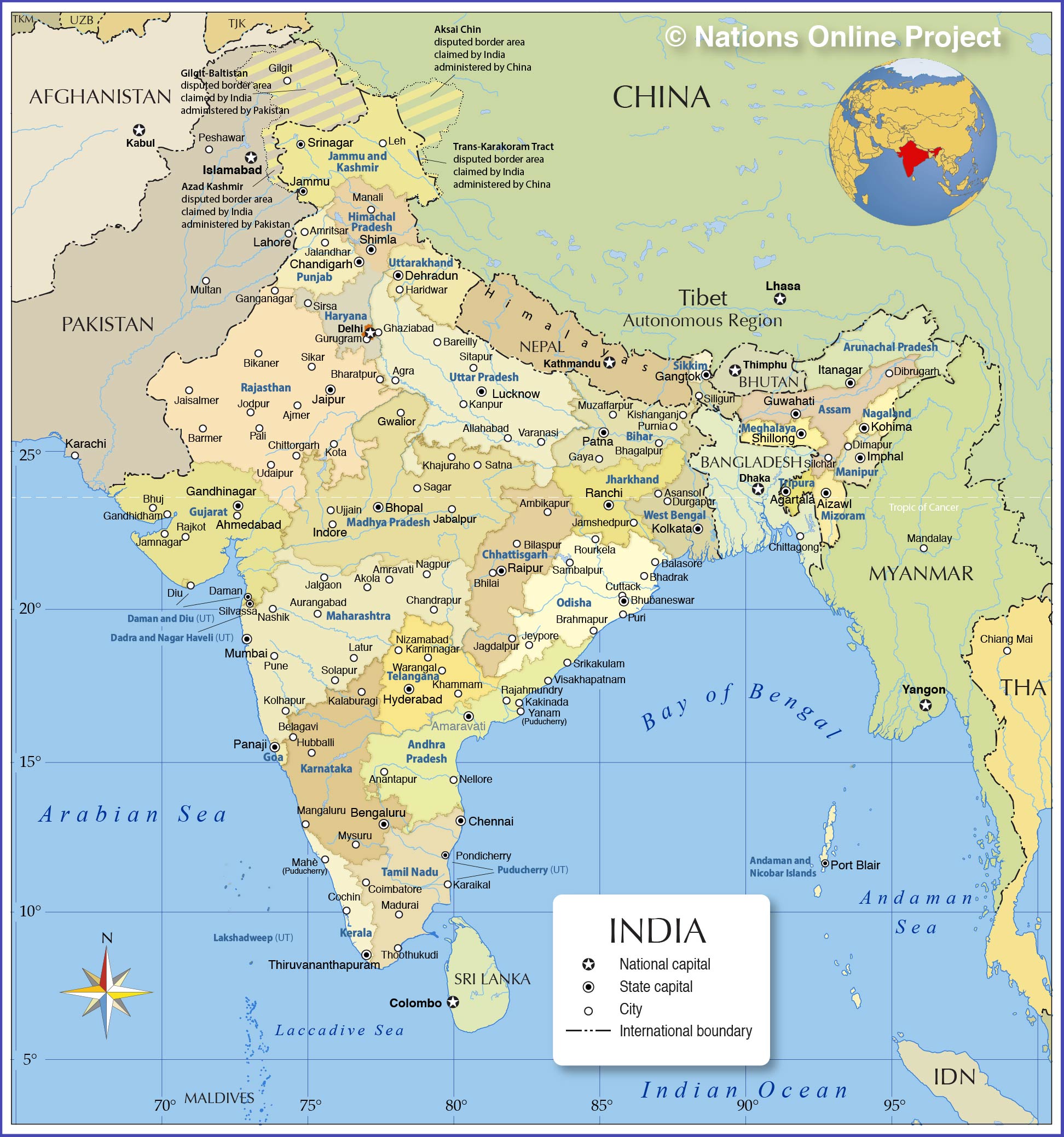
Political Map of India with States - Nations Online Project
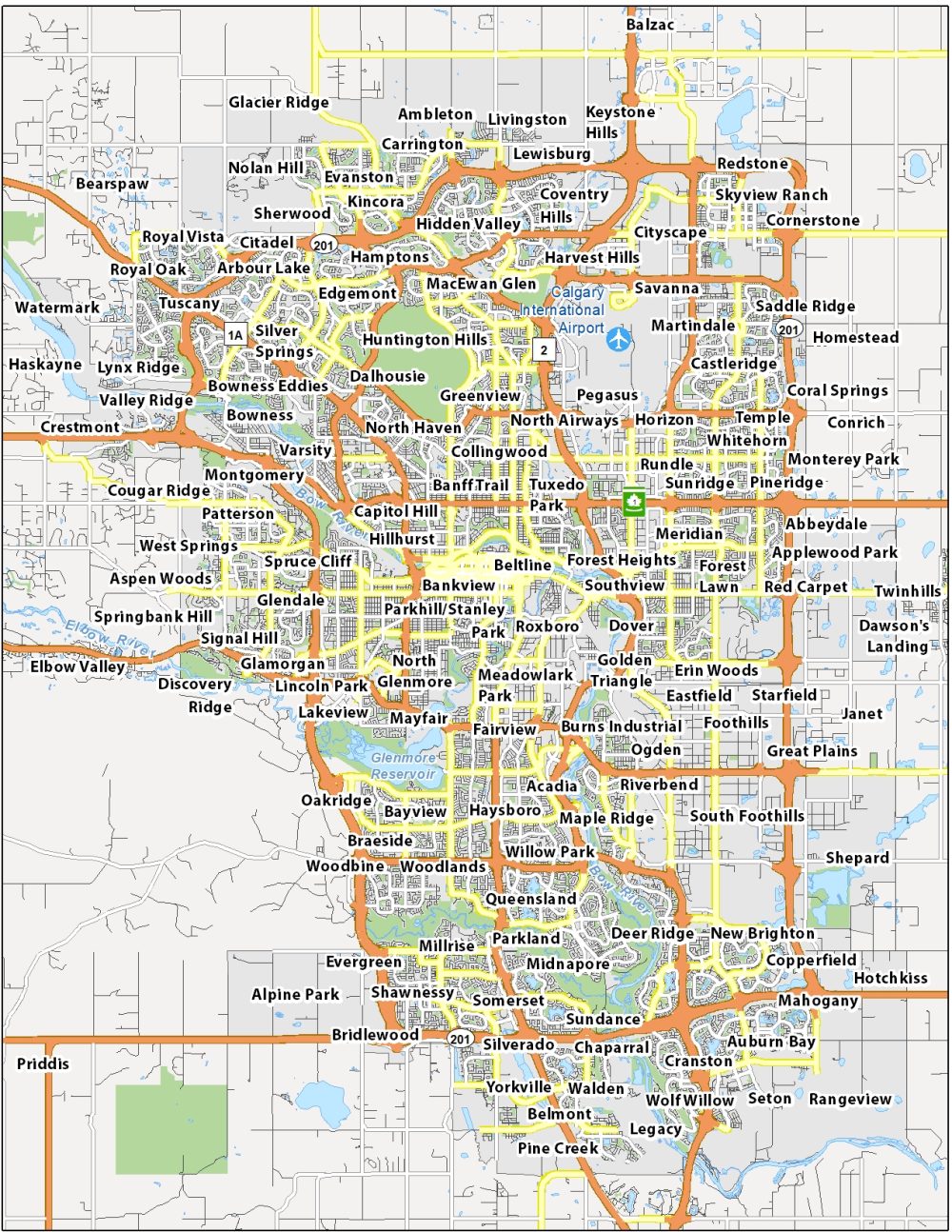
Map of Calgary, Canada - GIS Geography