Unveiling Iran: A Deep Dive Into Its Geography And Regions
The map of Iran region reveals a nation of immense geographical diversity, historical depth, and strategic importance, serving as a critical crossroads between continents and cultures. From its ancient administrative divisions to its modern provincial structure, understanding Iran's territorial organization is key to appreciating its complex identity. This article delves into the intricate layers of Iran's geography, history, and political landscape, offering a comprehensive exploration of its regions.
Often referred to officially as the Islamic Republic of Iran, this vast country, situated at the heart of the Middle East, is a land shaped by its unique position. It stretches between the azure waters of the Caspian Sea to the north and the vital maritime routes of the Persian Gulf, the Strait of Hormuz, the Gulf of Oman, and the Arabian Sea to the south. Its location at the crossroads of Central and South Asia, the Arab states, and the broader Middle East makes it a pivotal player in regional and global dynamics, a fact vividly illustrated by any comprehensive map of Iran region.
Table of Contents
- Unveiling the Map of Iran Region: A Geographic Tapestry
- Historical Evolution of Iran's Administrative Divisions
- Topography and Climate: A Land of Contrasts
- Iran's Strategic Location and Regional Significance
- Mapping Iran's Infrastructure and Connectivity
- Economic Insights: Provinces and GDP
- Navigating Modern Mapping of Iran
- Geopolitical Dynamics and the Map of Iran Region
- Conclusion: Iran, A Land of Layered Complexity
Unveiling the Map of Iran Region: A Geographic Tapestry
To truly appreciate the "map of Iran region," one must first grasp its fundamental geographic characteristics. Iran is not merely a country but a vast expanse, covering an area of 1,648,195 square kilometers (636,372 sq mi). To put this into perspective, it is smaller than Libya but notably larger than Egypt, positioning it as one of the largest nations in the Middle East. Its geographical footprint extends across diverse terrains, from towering mountain ranges to arid deserts and fertile coastal plains, each contributing to its unique character.
- Religious Leader Of Iran
- Did Isreal Attack Iran
- Does Iran Have An Air Force
- Iran Us Conflict
- Iran War With Usa
The country's borders are a testament to its strategic position. To the north, it shares a significant coastline with the Caspian Sea, a crucial inland body of water. To the south, its extensive coastline embraces the Persian Gulf, the Strait of Hormuz, the Gulf of Oman, and the Arabian Sea, all vital for global trade and energy routes. Land borders connect Iran with a multitude of neighbors: Iraq and Turkey to the west, Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, Turkmenistan to the northeast, and Afghanistan and Pakistan to the east. This complex web of borders underscores Iran's role as a nexus of various geopolitical interests and cultural exchanges, making the map of Iran region a crucial tool for understanding regional dynamics.
Historical Evolution of Iran's Administrative Divisions
The current political map of Iran, illustrating its 31 provinces with their capitals and the national capital, Tehran, is the culmination of centuries of administrative evolution. Understanding this progression is vital for anyone examining the "map of Iran region" from a historical perspective.
The 1937 Territorial Subdivision Act
A significant milestone in Iran's administrative history was the "Territorial Subdivision Act of 1316 Š./1937 (Qānūn-e taqsīmāt-e kešvar)." This act, implemented between 1937 and 1960, fundamentally reshaped the country's internal organization. Prior to this, Iran's territory was divided into ten distinct administrative regions. For instance, what was known as Region 7, or the "Seventh Province," corresponded directly to the present-day Fars province. This historical division highlights a continuous effort by the Iranian state to effectively govern its vast and diverse territories, adapting its administrative boundaries over time to better suit its needs. The evolution of these boundaries is a fascinating aspect of the map of Iran region's historical narrative (پیشینه تقسیمات کشوری ایران).
Modern Provincial Structure
Today, Iran is divided into 31 provinces, each officially known as an ostân (استان). Each province is governed from a local center, which is typically the largest city within that province. This central city is referred to as the capital, or markaz (مرکز in Persian), of that particular province. This structure ensures a localized governance approach, with each provincial capital serving as a hub for administration, commerce, and culture. Checking a political map of Iran today allows one to locate all these provinces and their respective capitals, offering a clear and detailed view of the contemporary administrative "map of Iran region."
Topography and Climate: A Land of Contrasts
Iran exhibits remarkable climatic diversity, a direct consequence of its varied topography and vast geographic position. Most regions experience an arid or semi-arid climate, characterized by low precipitation. Annual rainfall averages less than 250mm across much of the country, leading to vast desert landscapes. However, the Caspian coastal region in the north stands in stark contrast, receiving significantly higher amounts of rainfall, often exceeding 1,000mm annually, supporting lush forests and agricultural lands.
The country is home to two major deserts that dominate its central and eastern parts. The Kavir Desert, also known as Dasht-e Kavir, stretches across the central region, a vast salt desert known for its extreme temperatures and barren landscape. To the east lies the Lut Desert (Dasht-e Lut), renowned for being one of the hottest and driest places on Earth, with unique geological formations known as yardangs. These deserts are defining features on any detailed map of Iran region, illustrating the country's harsh yet beautiful natural environment.
Beyond the deserts, Iran's topography includes significant mountain ranges and limited lowlands. Parts of northwestern Iran are integral to the Armenian Highlands, topographically adjoining neighboring Turkey, Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia. This region is characterized by rugged mountains and high plateaus. In contrast, Iran has only two significant expanses of lowlands: the Khuzestan Plain in the southwest, a fertile area historically important for agriculture and oil, and the Caspian Sea coastal plain in the north, a narrow strip of land between the Alborz mountains and the Caspian Sea, known for its high humidity and agricultural productivity. These diverse topographical features, from towering peaks to vast deserts and fertile plains, make the map of Iran region a study in geographical extremes.
Iran's Strategic Location and Regional Significance
Iran's geographical placement is arguably its most defining strategic asset. It lies at the crossroads between Central and South Asia, the Arab states, and the broader Middle East. This unique position has historically made it a bridge for trade, culture, and power, influencing and being influenced by various civilizations. Its extensive coastline on the Gulf of Oman, Persian Gulf, and Caspian Sea further amplifies its maritime significance, providing crucial access to international waters and energy transportation routes.
Being part of both Asia and the larger region of Eurasia, but not Europe, positions Iran as a distinct geopolitical entity. Its proximity to key neighbors like Iraq, Azerbaijan, Armenia, Turkey, Kuwait, Pakistan, Afghanistan, and Turkmenistan means that developments within Iran inevitably have ripple effects across a wide geopolitical arc. This strategic centrality means that any detailed map of Iran region is not just a geographical representation but a geopolitical diagram, illustrating complex relationships and strategic interests that extend far beyond its borders.
Mapping Iran's Infrastructure and Connectivity
Modern maps of Iran offer much more than just geographical boundaries; they provide a comprehensive overview of the country's infrastructure and connectivity. These diverse map collections are invaluable resources for anyone interested in Iran, detailing its major regions, key infrastructure, and even historical landmarks. For instance, a large detailed map of Iran typically shows cities, towns, highways, roads, railroads, airports, and seaports, illustrating the arteries that connect the nation.
Air travel, for example, plays a crucial role in internal and external connectivity. As of 2013, Iran had approximately 319 airports, with the biggest and busiest serving as critical hubs for passenger and cargo transport. An "Iran airports map" would highlight these vital points, demonstrating the reach of the country's aviation network. Beyond airports, the intricate network of main roads, secondary roads, and railroads connects the vast provinces, facilitating trade, travel, and communication across challenging terrains. These infrastructure details on the map of Iran region are essential for understanding its economic and social fabric.
Economic Insights: Provinces and GDP
The economic landscape of Iran is as varied as its geography, with each province contributing uniquely to the national economy. Economic maps, such as those depicting "provinces of Iran by contribution to national GDP in 2014" or "provinces of Iran by GDP per capita in 2012," offer crucial insights into regional economic disparities and strengths. These maps highlight how different regions specialize in various sectors, from oil and gas in Khuzestan to agriculture in the Caspian plains, and industrial activities in central provinces like Tehran and Isfahan.
Understanding the economic distribution across the map of Iran region is vital for policymakers, investors, and researchers. It reveals the concentration of wealth, resources, and development, providing a clearer picture of the country's economic backbone and the challenges and opportunities for balanced regional growth. The capital city of each province, the markaz, often serves as the economic engine for its surrounding area, attracting investment and fostering local industries.
Navigating Modern Mapping of Iran
The advancement in geographic information systems (GIS) and digital mapping technologies has revolutionized how we interact with and understand the "map of Iran region." Modern mapping platforms have automated the entire process of turning geographic data into map graphics, leading to higher quality, faster, and more cost-effective map creation than ever before. Platforms like Maphill allow users to explore the same area from many different perspectives, offering a wide variety of map types and styles, from physical to political, and even satellite imagery.
These contemporary maps of Iran contain actual borders of Iran and its regions on the world map, main cities with names in both English and local languages, and a comprehensive transport network. Many modern mapping applications feature a tiled structure, where map tiles are loaded dynamically as users interact with the map, ensuring a smooth and responsive experience. The ability to interact with the map and its various layers, viewing Iran in 2D projection, offers an unparalleled level of detail and customization, making complex geographical information accessible to a general audience and specialists alike.
Geopolitical Dynamics and the Map of Iran Region
The "map of Iran region" is not just a static representation of land and borders; it is a dynamic canvas upon which geopolitical tensions and strategic maneuvers play out. Iran's nuclear program and military infrastructure have been points of international focus, leading to various reported incidents. For instance, historical reports and analyses have detailed events such as "Operation Rising Lion" on June 13, 2025, which reportedly targeted Iran’s missile and nuclear program. Such events, whether confirmed or alleged, underscore the critical importance of understanding the precise locations of key military and nuclear facilities within Iran.
Interactive maps are often utilized to highlight the locations of direct attacks attributed to various actors on Iranian territory, alongside Iran's key military and nuclear facilities. These maps serve as vital tools for geopolitical analysis, illustrating the sensitive nature of the region and the strategic importance of specific sites. While the geological map of Iran clearly places it in the Middle East, a region often associated with instability, it's important to note that, unlike some of its neighbors, Iran has historically maintained a degree of internal stability, a factor that can influence various aspects, including tourism.
Regional Stability and Tourism
Despite the broader geopolitical complexities of the Middle East, Iran has often enjoyed a level of complete stability within its borders, making it a viable destination for tourists. This internal stability, in contrast to some other countries in the region, is a significant factor for visitors planning to explore Iran's rich cultural heritage, ancient sites, and diverse natural landscapes. The ability to travel safely across its provinces, from the historical wonders of Fars (Region 7 in old divisions) to the bustling capital of Tehran, is a testament to this stability. The map of Iran region, therefore, also serves as a guide for exploration, inviting travelers to discover its hidden gems.
Conclusion: Iran, A Land of Layered Complexity
The "map of Iran region" tells a story of a nation deeply rooted in history, shaped by its unique geography, and navigating a complex geopolitical landscape. From the historical administrative divisions of 1937 to the modern 31 provinces, and from its arid deserts to its fertile Caspian coast, Iran is a land of profound contrasts and strategic importance. Its position at the crossroads of continents, its rich natural resources, and its evolving infrastructure all contribute to its multifaceted identity.
Exploring the various maps of Iran, whether historical, political, or topographical, offers an invaluable window into understanding this ancient yet modern nation. We encourage you to delve deeper into these fascinating details, perhaps by exploring interactive maps online or researching specific regions mentioned. What aspects of the map of Iran region do you find most intriguing? Share your thoughts in the comments below, or explore our other articles on regional geography and geopolitics to broaden your understanding of the world.
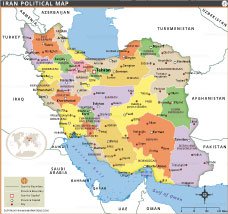
Where is Iran?, Where is Iran located?

A Crossroads Of History And Culture: Exploring The Map Of Turkey And
Arabian peninsula,iraq,iran hi-res stock photography and images - Alamy