Unveiling Iran's Population Dynamics: A Deep Dive Into Demographic Shifts
Iran, often referred to as Persia or the Islamic Republic of Iran, stands as a pivotal nation in Western Asia, not only for its rich history and strategic geographical position but also for its significant and evolving demographic landscape. Understanding the "poblacion de iran" – the population of Iran – is crucial for grasping the country's socio-economic trajectory, its challenges, and its future potential. From its dramatic growth in the late 20th century to more recent shifts in birth rates and age distribution, Iran's population story is a complex tapestry woven with historical, cultural, and geopolitical threads.
This comprehensive article delves into the intricate details of Iran's population, drawing upon the latest available data and projections. We will explore its current size and global standing, trace its historical growth, analyze key demographic indicators such as age and gender distribution, and examine the external and internal factors that shape its human landscape. By providing a clear and well-researched overview, we aim to offer valuable insights into the dynamic forces influencing one of the Middle East's most populous nations.
Table of Contents
- Iran's Place on the Global Population Map
- A Historical Look at Iran's Population Growth
- Shifting Sands: The Recent Decline in Birth Rates
- Demographics Unpacked: Age and Gender Distribution
- Migration Patterns: Iran's Immigrant Landscape
- External Factors Influencing Iran's Population
- Projections and Future Outlook for Iran's Population
- Why Understanding Iran's Population Matters
Iran's Place on the Global Population Map
To truly appreciate the scale of the "poblacion de iran," it's essential to contextualize it within the global demographic framework. As of November 2024, Iran's population stands at approximately 91.5 million people, with projections indicating a slight increase to 91.57 million for the full year 2024 and further to 92.42 million by July 1, 2025. These figures solidify Iran's position as a significantly populated country on the world stage. For instance, the total population for Iran in 2023 was recorded at 90,608,707, reflecting a consistent growth trajectory from 89,524,246 in 2022, both showing a 1.21% increase from the previous year. This places Iran at number 17 in the list of countries by population, accounting for approximately 1.12% to 1.123% of the total world population.
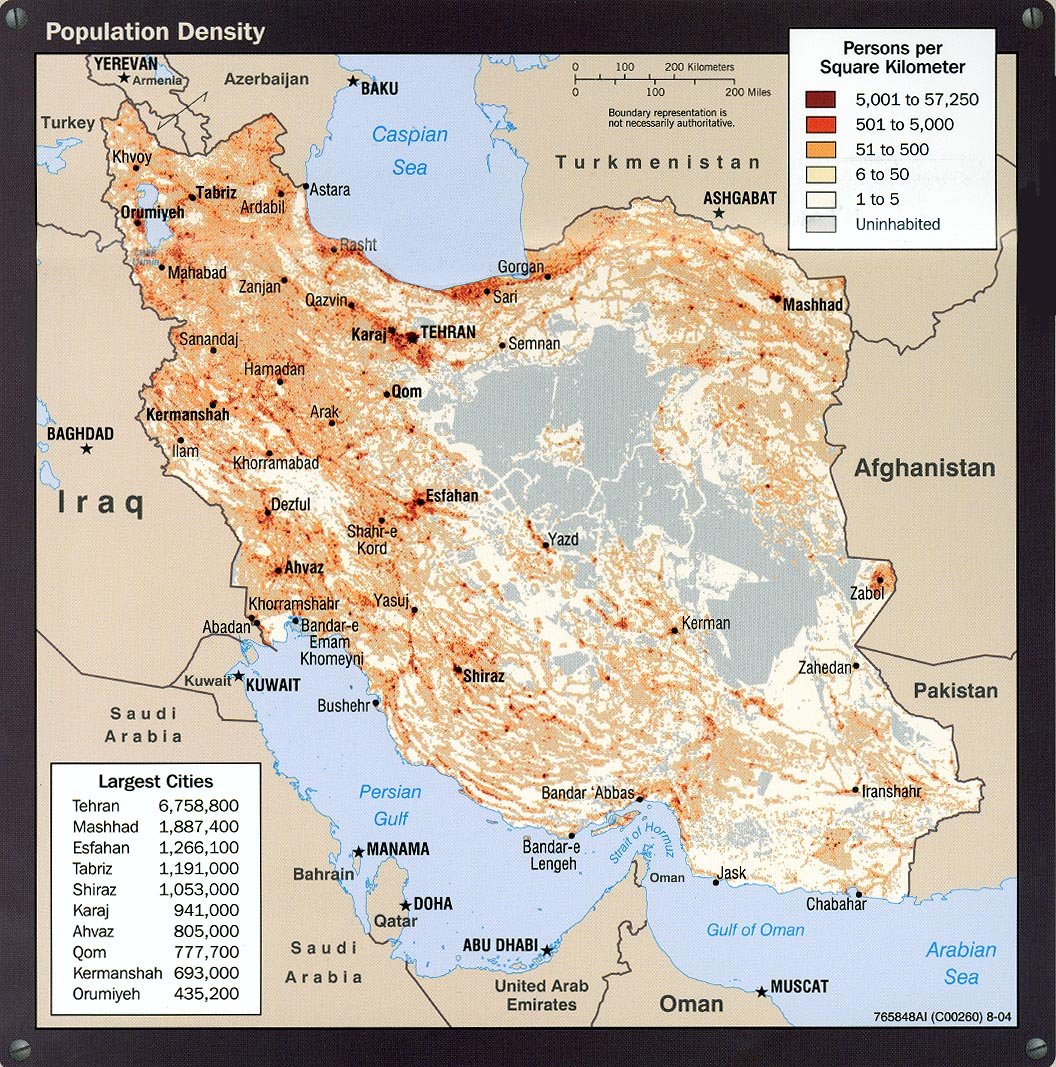
Geographically, Iran is a vast nation, situated strategically in Western Asia. It shares its northern borders with Turkmenistan, Azerbaijan, and Armenia, with the expansive Caspian Sea providing a natural boundary to Kazakhstan and Russia further north. To its east, Iran is bordered by Pakistan and Afghanistan, while its southern coastlines meet the waters of the Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf. The total land area of Iran is approximately 1,628,550 km² (or 628,786 sq mi), making it a large country by landmass. Despite its substantial population, Iran maintains a moderate population density of about 57 people per km² (147 people per mi²), suggesting that while densely populated in urban centers, vast swathes of its territory remain less inhabited. This balance between a large population and a considerable land area contributes to its moderate density, allowing for varied geographical and demographic patterns across the nation.
A Historical Look at Iran's Population Growth
The story of the "poblacion de iran" is one of remarkable expansion, particularly during the latter half of the 20th century. Following the Islamic Revolution in 1979, when the population was little over 33 million inhabitants, Iran experienced a dramatic surge in its numbers. This period of rapid demographic expansion saw the population reach approximately 80 million by 2016, and it has continued to grow steadily since then, surpassing 90 million in recent years. This significant increase was not accidental but rather the result of a confluence of factors that profoundly impacted the nation's vital statistics.
Primarily, the dramatic growth can be attributed to a notable decrease in the mortality rate, coupled with a sustained increase in the birth rate. Advances in healthcare, improved sanitation, and broader access to medical services contributed to a decline in infant and child mortality, allowing more individuals to survive into adulthood. Simultaneously, social and cultural factors, often influenced by post-revolutionary policies, encouraged larger families, leading to a higher fertility rate. This combination created a demographic momentum that propelled Iran's population upwards at an unprecedented pace for several decades. The youthful demographic structure resulting from this period of high growth laid the foundation for the current population size, even as more recent trends indicate a shift in these dynamics.
Shifting Sands: The Recent Decline in Birth Rates
While the "poblacion de iran" experienced robust growth throughout the late 20th century, recent years have witnessed a significant shift in its demographic trajectory: a progressive decline in the birth rate. This change marks a crucial turning point, indicating that the rapid expansion of previous decades is now moderating. Studies and recent data highlight this trend, projecting that Iran's rate of population growth will continue to slow in the coming years. For instance, the average number of children per woman dropped to 1.71 by 2020, a figure considerably lower than the replacement level needed to maintain a stable population in the long term.
This decline in fertility is a multifaceted phenomenon, likely influenced by various socio-economic factors. Urbanization, increased access to education for women, changing family planning norms, and economic pressures can all contribute to couples choosing to have fewer children. As the country develops and its population becomes more urbanized, these trends are often observed globally. The implications of a slowing growth rate are profound, potentially leading to an aging population structure in the future, with a larger proportion of elderly dependents and a smaller working-age population. This demographic transition presents both opportunities and challenges for policymakers, requiring careful planning for healthcare, social security, and economic productivity in the decades to come.
Demographics Unpacked: Age and Gender Distribution
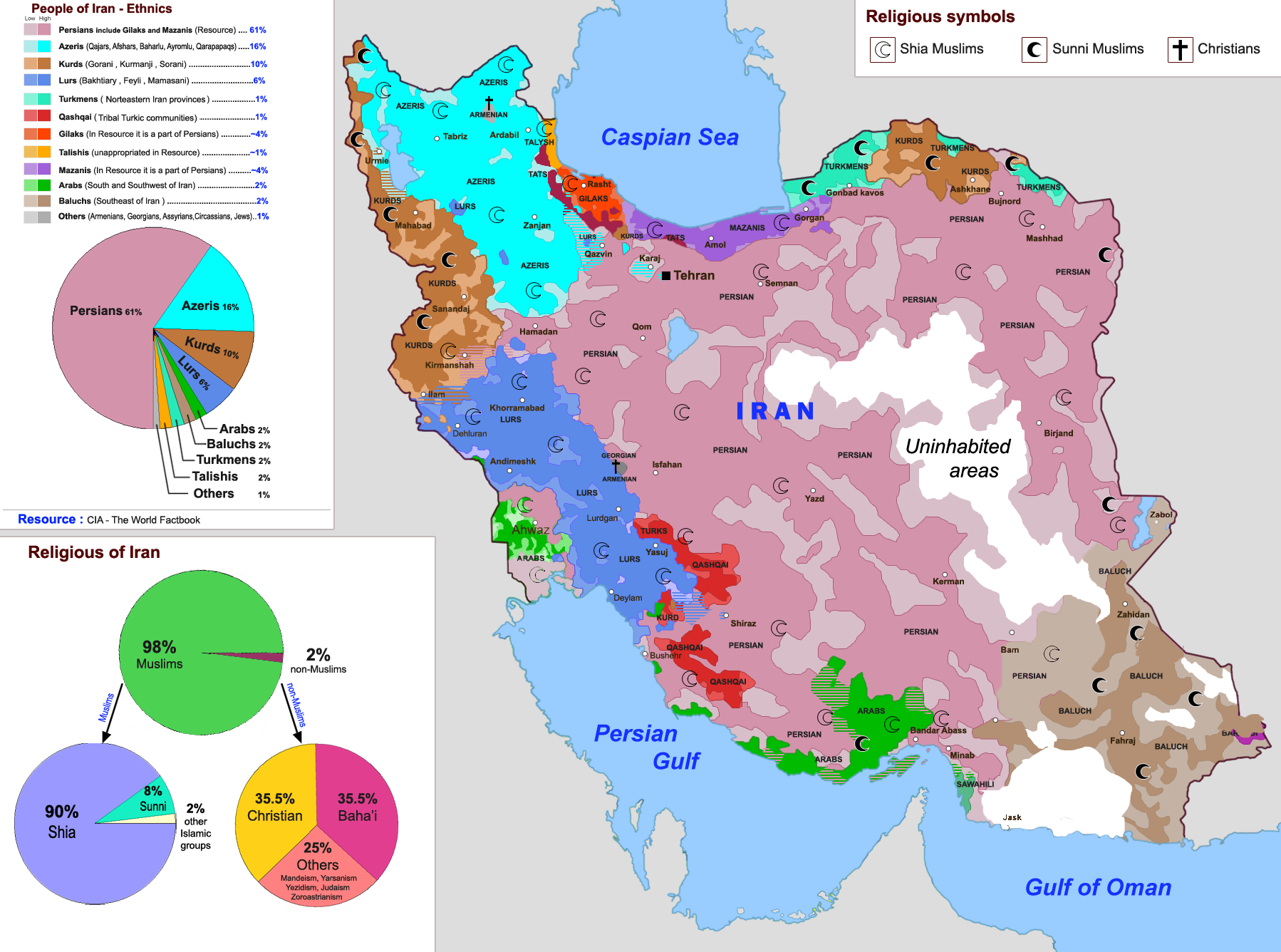
Beyond the sheer numbers, understanding the internal structure of the "poblacion de iran" provides deeper insights into its societal characteristics and future potential. The age and gender distribution within a population, often visualized through a population pyramid, reveals much about a country's past trends and future challenges. Iran's demographic profile exhibits some particularly interesting features.
The Youthful Core: Under 15 Population
A notable characteristic of Iran's population pyramid is its relatively youthful structure. Data indicates that approximately 25% of Iran's inhabitants are under 15 years of age. This substantial proportion of young people signifies a large cohort entering their productive years in the near future. A youthful population can be a significant asset, providing a large labor force and driving economic growth through consumption and innovation. However, it also presents challenges related to education, employment, and the provision of adequate social services for a growing number of young citizens seeking opportunities.
The presence of such a large youth demographic is a legacy of the high birth rates experienced in the decades following the 1979 revolution. While the birth rate has recently declined, the sheer number of individuals born during those high-fertility periods ensures that the youth segment remains a dominant force in Iran's demographic composition for the foreseeable future. This dynamic underscores the importance of investing in youth development, vocational training, and job creation to harness this demographic dividend effectively.
A Unique Gender Balance: Male Majority
One curious and somewhat unusual demographic fact about the "poblacion de iran" is that, unlike the majority of countries worldwide, the male population is slightly superior to the female population. Current figures indicate that males constitute approximately 50.7% of the population, while females make up 49.3%. While this difference might seem minor, it stands out against global trends where women often slightly outnumber men, particularly in older age groups due to higher life expectancy.
For instance, based on an earlier population clock value of 89,398,702, the male population was reported at 44,061,777. While the corresponding female number provided in the source (750,516) appears to be a clerical error given the overall population and percentage, the consistent mention of a slight male majority across various data points confirms this unique characteristic. The reasons for this slight imbalance can be complex, potentially influenced by birth sex ratios, differential mortality rates across age groups, or even historical migration patterns. Regardless of the underlying causes, this particular gender distribution is a distinctive feature of Iran's demographic landscape.
Migration Patterns: Iran's Immigrant Landscape
The "poblacion de iran" is not solely shaped by births and deaths; migration also plays a role, albeit a less dominant one compared to some other nations. According to the latest immigration data published by the UN, immigrants constitute approximately 3.33% of Iran's total population. This percentage positions Iran as the 108th country in the world by the percentage of its immigrant population. While this figure indicates a relatively modest proportion of foreign-born residents compared to countries with high immigration rates, it still represents a significant number of individuals who have chosen Iran as their home.
Iran has historically been a host to a considerable number of refugees, particularly from neighboring Afghanistan, due to decades of conflict and instability in that country. These communities have often integrated into Iranian society, contributing to its diverse cultural and economic fabric. Understanding the immigrant landscape is important for policymakers to ensure proper integration, access to services, and to manage potential social and economic impacts. While the focus of this article is on the overall "poblacion de iran," the presence of an immigrant population adds another layer of complexity and richness to its demographic story.
External Factors Influencing Iran's Population
The trajectory of the "poblacion de iran" is not solely determined by internal demographic processes; it is also significantly influenced by a range of external factors, particularly economic and geopolitical pressures. These elements can have profound impacts on birth rates, mortality rates, and migration patterns, shaping the population's present and future.
Economic Pressures: Sanctions and Trade
One of the most impactful external factors on Iran's economy, and by extension its population, has been the imposition of severe international sanctions, particularly by the United States. Starting in 2018, these sanctions were primarily enacted due to Iran's well-documented financing and sponsorship of terrorism. The stated American objective is to suffocate the Iranian economy by halting its trade with the rest of the world. Such economic pressures can have far-reaching demographic consequences.
A constrained economy can lead to reduced employment opportunities, higher inflation, and a decline in living standards. These conditions often influence family planning decisions, potentially contributing to the observed drop in birth rates as couples face greater economic uncertainty. Furthermore, economic hardship can spur emigration, particularly among skilled workers and young professionals seeking better prospects abroad. While the Iranian company Iran Khodro continues to manufacture vehicles, representing a segment of the domestic economy, the overall impact of sanctions on various sectors, including healthcare and access to essential goods, can indirectly affect public health and mortality rates, thereby influencing the "poblacion de iran" in subtle yet significant ways.
Geopolitical Tensions and Displacement
The geopolitical context of the region also plays a critical role in shaping Iran's population dynamics. The broader Middle East is frequently marked by instability and conflict, and Iran is not immune to these pressures. For example, a recent update from April 13, 2024, mentioned by the I.R. Iran Mission to the UN, NY, and a specific report from June 19, 2025, indicate that people continue to flee Tehran, the capital of Iran, amidst reports of Israeli airstrikes showing no signs of stopping. While this specific event is projected into the future in the provided data, it highlights how ongoing geopolitical tensions and potential conflicts can lead to internal displacement and, in some cases, international migration.
Such events, whether actual or threatened, can disrupt daily life, impact infrastructure, and create an environment of uncertainty that affects demographic decisions. Displacement can lead to temporary or permanent changes in population distribution within the country, putting strain on resources in host areas. Prolonged instability can also indirectly affect birth rates and mortality rates due to stress, lack of access to healthcare, or disruptions in food supply chains. Therefore, geopolitical developments are crucial considerations when analyzing the current state and future projections of the "poblacion de iran."
Projections and Future Outlook for Iran's Population
Looking ahead, the "poblacion de iran" is projected to continue its growth, albeit at a slower pace than in previous decades. As of July 1, 2025, the total population in Iran is projected to reach approximately 92,417,681, or 92.42 million. For the year 2024, the projection stands at 91,567,738, or 91.57 million people. These projections, alongside the current annual growth rate of 0.859%, suggest a continued, though decelerating, expansion of the population. The slowing growth rate, primarily driven by the significant drop in the birth rate, indicates a demographic transition towards an older population structure in the long run.
The implications of this slowing growth are multi-faceted. On one hand, a slower growth rate could alleviate pressure on resources such as water, housing, and employment, which have been strained by rapid population expansion. On the other hand, it means a potentially aging population, which will necessitate robust social security systems, expanded healthcare for the elderly, and potentially a smaller working-age population to support them. Policymakers in Iran will need to strategically plan for these demographic shifts, adapting economic and social policies to ensure sustainable development and well-being for all age groups. The future of the "poblacion de iran" will largely depend on how these internal demographic trends interact with the ongoing economic and geopolitical realities.
Why Understanding Iran's Population Matters
Understanding the "poblacion de iran" is far more than an academic exercise in counting heads; it is fundamental to comprehending the nation's present challenges and future trajectory. The sheer size and dynamic nature of Iran's population have profound implications across various sectors, from economic development and urban planning to social welfare and geopolitical influence.
Economically, a large and relatively young population presents both opportunities and demands. A significant workforce can drive industrial growth and innovation, as exemplified by entities like the Iran Khodro vehicle factory. However, it also necessitates robust job creation to prevent unemployment and social unrest. Socially, the youthful demographic requires substantial investment in education and healthcare, while the projected aging trend will soon demand comprehensive elderly care and pension reforms. Geopolitically, the size and composition of Iran's population contribute to its regional standing and influence, affecting everything from military recruitment to diplomatic leverage. Therefore, accurate and up-to-date demographic data is indispensable for informed policy-making, strategic planning, and fostering a stable and prosperous future for the Islamic Republic of Iran and its people.
Conclusion
In summary, the "poblacion de iran" is a vibrant and evolving demographic force, having experienced dramatic growth in the latter half of the 20th century, reaching over 90 million in recent years. This expansion was fueled by declining mortality and high birth rates, leading to a youthful population where about 25% are under 15. Uniquely, Iran also exhibits a slight male majority. However, recent years have seen a significant drop in birth rates, signaling a slower growth trajectory for the future, with projections for 2024 at around 91.5 million and 2025 at 92.4 million.
External factors, particularly severe economic sanctions and ongoing geopolitical tensions, continue to exert influence, potentially impacting internal migration and future demographic choices. As Iran navigates these complex dynamics, understanding its population shifts is paramount for addressing socio-economic challenges and harnessing its human capital. We encourage you to share your thoughts on the implications of these demographic changes in the comments below. What do you believe are the biggest opportunities or challenges for Iran given its population trends? Explore more articles on our site to deepen your understanding of global demographics and their far-reaching impacts.
Irán: población | La guía de Geografía
The Map of Iran coloring page - Download, Print or Color Online for Free
Densidad de población en Irán – Recortes de Oriente Medio