Unveiling The Caspian Sea: Iran's Northern Gateway
The Caspian Sea, often hailed as the world's largest inland body of water, holds immense geographical, economic, and cultural significance, especially for Iran. For centuries, its vast expanse has shaped the landscapes, livelihoods, and history of the nations bordering it. When we delve into a Caspian Sea Iran map, we uncover not just a body of water, but a vibrant region integral to Iran's identity and strategic interests. This unique endorheic basin, nestled at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, offers a fascinating study of natural wonders and human interaction.
Understanding the Caspian Sea's relationship with Iran goes beyond mere geography; it encompasses historical cartography, economic prospects, and the distinctive cultural fabric of Iran's northern provinces. From ancient maps depicting it as the "middle of the world" to modern satellite imagery highlighting its energy potential, the Caspian Sea continues to be a focal point for exploration and development. This article will guide you through the intricate details of the Caspian Sea as seen through the lens of Iran, exploring its unique characteristics, historical context, and contemporary importance.
Table of Contents
- The Caspian Sea: A Geographical Marvel
- Iran's Strategic Connection to the Caspian Sea
- Historical Depictions and Modern Significance
- Geopolitical Landscape: Bordering Nations and Resources
- Economic Prospects: Energy and Trade
- Navigating Iran's Caspian Coast: Cities and Infrastructure
- The Caspian Sea in Broader Iranian Geography
- Frequently Asked Questions About the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea: A Geographical Marvel
The Caspian Sea is a geographical anomaly, a colossal body of water that defies easy categorization. It is an endorheic basin, meaning it is a closed drainage basin that retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water, such as oceans. This unique characteristic contributes to its distinct hydrological and ecological features. Its location is equally fascinating: it lies between Europe and Asia, specifically east of the Caucasus Mountains, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia, south of the fertile plains of Southern Russia in Eastern Europe, and north of the mountainous Iranian Plateau. This strategic position has historically made it a significant crossroads for trade, culture, and civilizations.
An Endorheic Basin at a Crossroads
Situated about 500 km east of the Black Sea, the Caspian Sea acts as a natural divide and bridge between southeastern Europe and western Asia. Its vastness spans nearly 750 miles (1,200 km) from north to south, although its average width is a more modest 200 miles (320 km). This immense stretch of water is bordered by five countries: Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Iran, Azerbaijan, and Russia. Each of these nations shares a unique relationship with the sea, influencing its environmental management, resource allocation, and geopolitical dynamics. The interaction of these diverse regions – from the cold steppes of Russia and Kazakhstan to the arid deserts of Turkmenistan and the rugged mountains of Iran and Azerbaijan – creates a rich tapestry of climates and ecosystems around the Caspian.
Size and Salinity: A Lake or a Sea?
Debates often arise regarding whether the Caspian Sea should be classified as the world's largest lake or a true sea. With an astounding area of 371,000 km² (without the Garabogazköl Bay), it is undeniably the largest enclosed inland body of water on Earth. Its sheer scale is such that it forms waves along its shores, much like an ocean, a characteristic that further blurs the lines of its classification.
The composition of the Caspian Sea's water also adds to its intrigue. Unlike typical freshwater lakes, the Caspian is saline, though its salinity levels vary significantly across its expanse. The northern parts, fed by the Volga River, are almost fresh, gradually becoming saltier towards the south. This gradient in salinity supports a diverse range of aquatic life, from freshwater species in the north to more salt-tolerant organisms in the deeper, southern basins. This unique hydrological profile underscores the Caspian Sea's exceptional nature, making it a subject of continuous scientific study and environmental concern.
Iran's Strategic Connection to the Caspian Sea
For Iran, the Caspian Sea is more than just a northern border; it is a vital geographical and economic artery. A Caspian Sea Iran map clearly illustrates this intimate connection, showing how the sea defines the northern frontier and influences the climate, culture, and economy of the adjacent Iranian provinces. Iran's rugged terrain, characterized by a mix of deserts and plains along coastal areas, finds a stark contrast in the lush, verdant landscapes of its Caspian coastline.
The Iranian Plateau and Coastal Plains
Iran is geographically diverse, marked by three major mountain chains. The Elburz Mountains, in particular, lie prominently in the north, very close to the Caspian Sea. This mountain range acts as a significant barrier, trapping moisture from the Caspian and contributing to the region's unique climate. While much of Iran is dominated by the high Iranian Plateau and arid conditions, the country possesses only two major expanses of lowlands: the Khuzestan plain in the southwest and the Caspian Sea coastal plain in the north. This northern lowland, a narrow strip nestled between the sea and the towering Alborz mountains, is exceptionally fertile and densely populated, standing in stark contrast to the vast interior deserts.
Northern Iran: A Distinctive Region
Caspian Iran, also known as Northern Iran, is renowned for its breathtaking natural beauty. This region along the coast of the Caspian Sea is characterized by forested coastal plains that rise quickly into the majestic Alborz Mountains. The lush greenery, abundant rainfall, and mild climate make it a popular destination for both local and international tourists. The region consists of three key provinces: Gilan, Mazandaran, and Golestan. These provinces are culturally rich, with distinct local traditions, cuisines, and languages that set them apart from other parts of Iran. Cities like Nowshahr, with a population of about 50,000 people, dot the coastline, serving as important ports and urban centers for the region's agricultural and fishing industries. The proximity to the sea also influences the local architecture and lifestyle, creating a unique blend of mountain and coastal cultures.
Historical Depictions and Modern Significance
The Caspian Sea has long captured the imagination of cartographers and explorers. Historical maps offer invaluable insights into how this vast body of water was perceived and depicted across different eras. For instance, the 17th-century CE world map by Sadiq Isfahani famously placed the Caspian Sea in the "middle of the world map," underscoring its perceived centrality and importance in the global understanding of geography at the time. It should be noted that available versions of this map are often Safavid era copies of the original book, showcasing the enduring interest in this region through various historical periods. These historical maps, including a French map of the Persian Gulf from around the same period, highlight the long-standing European and Asian interest in the region's geography and trade routes.
Today, a Caspian Sea Iran map serves not just as a geographical reference but as a tool for understanding complex geopolitical and economic realities. Maps of Iran often dedicate sections to representing different aspects of its geography, acknowledging their essential role for travelers and researchers alike. The lack of variety in older Iranian maps has led to a modern push to provide diverse maps for different usages and interests, from detailed topographical maps to those focusing on infrastructure like Iran's rail network connecting major cities such as Tehran, Mashhad, Isfahan, and Shiraz. The Caspian Sea's consistent presence on these maps, alongside the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman, reaffirms its enduring significance in Iran's national identity and strategic planning.
Geopolitical Landscape: Bordering Nations and Resources
The Caspian Sea's unique status as an enclosed basin bordered by five nations – Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Iran, Azerbaijan, and Russia – creates a complex geopolitical landscape. The legal status of the Caspian Sea, whether it is a lake or a sea, has significant implications for resource sharing, particularly concerning its vast hydrocarbon reserves. If classified as a lake, resources would typically be divided equally among riparian states. If a sea, international maritime law, which usually grants exclusive economic zones, would apply. This debate has fueled decades of negotiations and has shaped the relationships between the bordering countries.
Iran's borders are extensive and diverse, touching Armenia and Azerbaijan in the northwest, Afghanistan and Pakistan in the east, and Iraq and Turkey in the west. This complex web of international boundaries, combined with its access to three major bodies of water – the Caspian Sea to the north, and the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman to the south – positions Iran as a pivotal player in regional and global geopolitics. The Caspian Sea, with its potential for oil and gas, adds another layer of strategic importance, making its demarcation and resource management a critical aspect of Iran's foreign policy and economic strategy.
Economic Prospects: Energy and Trade
The Caspian Sea region is widely recognized for its substantial energy prospects, particularly in oil and natural gas. The image "Iran southern caspian energy prospects 2004.jpg" and references to "Caspian sea oil and gas infrastructure" highlight the significant interest in extracting these valuable resources. For Iran, the development of its southern Caspian energy fields is a key component of its long-term economic strategy. While much of Iran's known oil and gas reserves are concentrated in the Persian Gulf, the Caspian offers an alternative and potentially lucrative source, reducing reliance on its southern fields and diversifying its energy portfolio.
Beyond hydrocarbons, the Caspian Sea facilitates trade and transportation among its littoral states. Its ports serve as crucial hubs for goods exchange, connecting Central Asia to European and Middle Eastern markets. For Iran, the Caspian Sea provides a northern gateway for trade, complementing its southern ports on the Persian Gulf. This dual access to major waterways enhances Iran's position as a regional trade corridor, allowing it to leverage its geographical advantage for economic growth and international cooperation. The development of port cities and related infrastructure along the Iranian Caspian coast is therefore essential for maximizing these economic opportunities.
Navigating Iran's Caspian Coast: Cities and Infrastructure
The Iranian coastline along the Caspian Sea is dotted with vibrant cities and developing infrastructure, essential for both local life and national interests. As mentioned, Nowshahr is an important city along the Caspian, known for its port activities. Other significant urban centers in the provinces of Gilan, Mazandaran, and Golestan also play crucial roles in the region's economy and culture. These cities serve as centers for agriculture, fishing, tourism, and trade, benefiting from the fertile plains and the sea's resources.
Infrastructure development in this region is critical. A Caspian Sea Iran map that displays Iran's rail network connecting major cities, including those in the north, underscores the efforts to integrate the Caspian region more fully into the national economic fabric. Improved transportation links, including roads and railways, facilitate the movement of goods and people, supporting economic growth and enhancing connectivity with the rest of Iran. The rugged terrain along the rim of the Caspian, a mix of deserts and plains, presents engineering challenges, but strategic investments continue to improve access and development along this vital northern rim.
The Caspian Sea in Broader Iranian Geography
To truly appreciate the significance of the Caspian Sea for Iran, one must view it within the context of Iran's overall geography. Iran is situated in both the northern and eastern hemispheres, a vast country with a diverse landscape. Its borders are extensive, touching Armenia, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, Kazakhstan, Russia, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Iraq, and Turkey. This broad geographical footprint, coupled with its access to three major bodies of water – the Caspian Sea to the north, and the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman to the south – makes Iran a nation of considerable geopolitical importance.
The Caspian Sea forms a distinct geographical and climatic zone in the north, contrasting sharply with the arid central plateau and the warm southern coasts. Key geographical features, such as the Alborz and Zagros mountain ranges, further define Iran's landscape. The capital city, Tehran, a bustling metropolis, serves as the economic and political center, but the influence of the Caspian Sea extends far beyond its immediate shores, impacting national policies related to environment, trade, and energy. The availability of various maps of Iran, including those focusing on specific regions or features, is crucial for understanding these intricate geographical relationships and their implications.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Caspian Sea
Here are some common questions about the Caspian Sea and its connection to Iran:
- What countries border the Caspian Sea?
The Caspian Sea is bordered by five countries: Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Iran, Azerbaijan, and Russia.
- Is the Caspian Sea a lake or a sea?
It is considered by many to be the largest lake in the world, being the largest enclosed inland body of water on Earth. However, due to its size, salinity, and wave formation, it often exhibits characteristics of a sea.
- How salty is the Caspian Sea?
The salinity of the Caspian Sea varies significantly. It is almost fresh in its northern parts, particularly near the Volga River delta, and becomes saltier towards the south.
- What are the main geographical features of Iran's Caspian region?
Iran's Caspian region, also known as Northern Iran, is characterized by forested coastal plains that quickly rise into the Alborz Mountains. It includes the provinces of Gilan, Mazandaran, and Golestan.
- What is the significance of the Caspian Sea for Iran?
For Iran, the Caspian Sea represents a vital northern border, a source of energy (oil and gas prospects), a gateway for trade, and a region of significant cultural and natural beauty. It also plays a role in Iran's geopolitical standing.
If you have any other questions about the Caspian Sea, its map, or other related topics, please let us know in the comments below. We will respond as soon as possible.
Caspian Sea Iran Map: A Concluding Perspective
The journey across a Caspian Sea Iran map reveals a dynamic and crucial relationship between a nation and one of the world's most extraordinary natural wonders. From its ancient depiction as the "middle of the world" to its modern role in energy and geopolitics, the Caspian Sea remains an indispensable part of Iran's identity and future. Its unique geographical characteristics, combined with the rich cultural tapestry of Northern Iran, make it a region of enduring fascination and strategic importance.
As Iran continues to develop its northern provinces and leverage its Caspian Sea access for economic growth and international engagement, understanding this vital connection becomes ever more critical. We hope this comprehensive exploration has provided you with valuable insights into the Caspian Sea's profound impact on Iran. Share your thoughts in the comments section below, or explore more of our articles on Iran's diverse geography and rich history. Your engagement helps us continue to provide valuable and well-researched content.
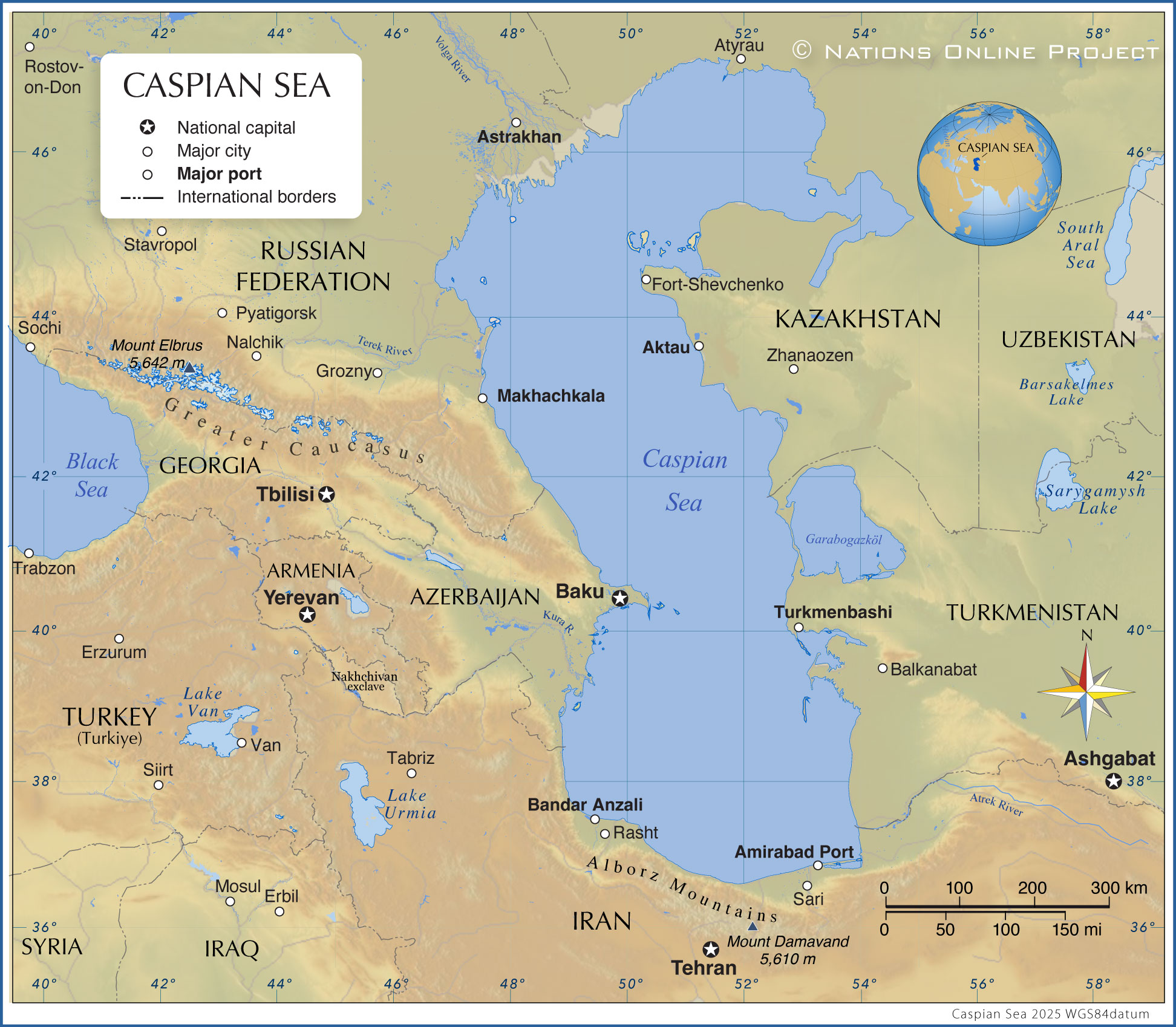
Map of the Caspian Sea - Nations Online Project

Map of Iran shows natural Caspian Sea habitats (yellow placemarks, 1
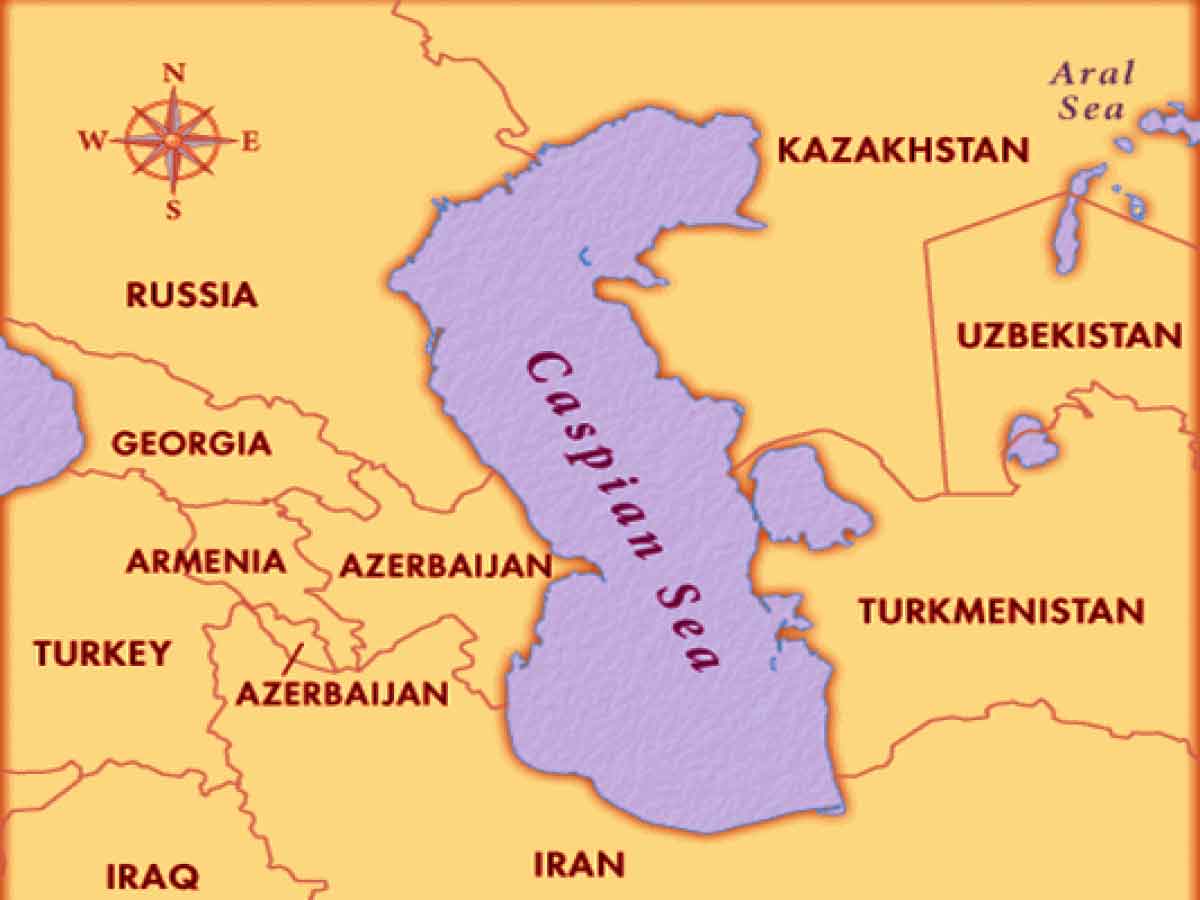
Caspian Sea - Iran Safar